
PTPA #011: Flavors of Product Management
Nov 20, 2022Read Time: 5 minutes.
We always talk about Product Management as THE role to get into. But the reality is that there are different flavors to it.
Data, Growth, Technical and just Product Management are the most common ones. In 2022, the search interest over time (popularity) doubled for the first three.
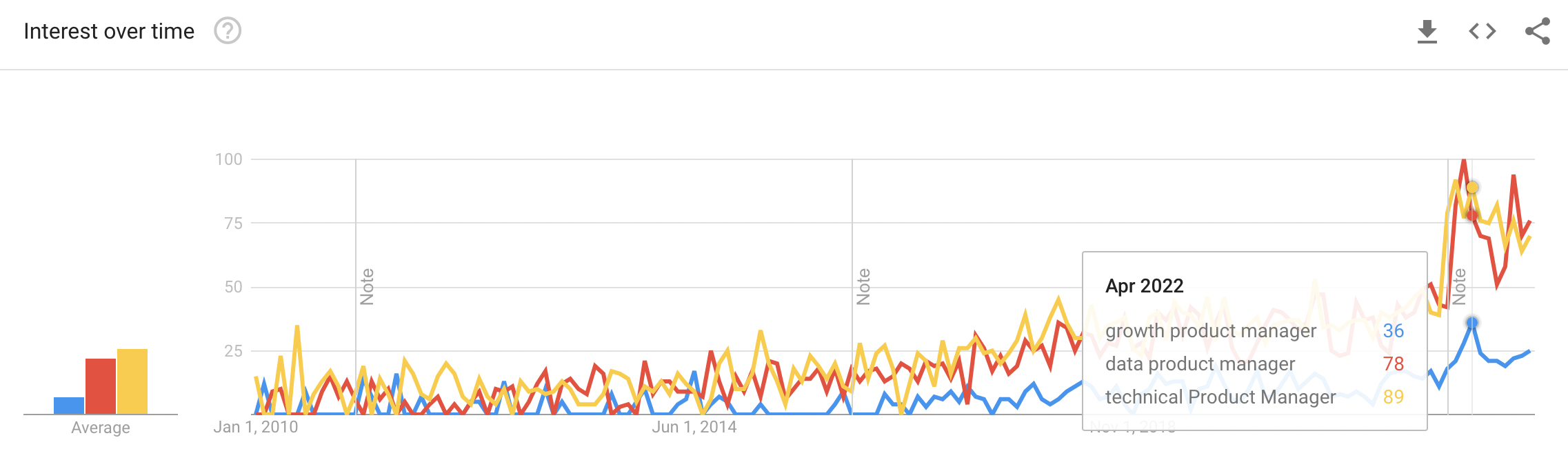
In short, here's what each of them focuses on:
- Product Manager → Make the product successful.
- Technical PM → Make the Product reliable, and scalable.
- Growth PM→ Experiment to make the business successful.
- Data PM → Align Product teams through data.
These definitions of Product Management flavors assume that there is a clear distinction between the different flavors of Product Management. In most companies, the roles will overlap.
Let's look at each one in detail.
1. Product Manager
At a high level, PMs can be compared to a COO or CSO.
Product Managers focus on customers and the business, on creating Vision, Strategy, and Planning. They define the "WHY" and the "WHAT" that needs to be built.
The "WHAT" that PMs answer, starts with a customer pain point that is deeply researched and justified.
PMs are constantly researching:
- Partners.
- Customers.
- Competitors.
- Market Trends.
- Business Models.
- Target Industries.
In their day to day, PMs are responsible for understanding goals and KPIs, as well as customers and their pain points. They take all those insights to create an MVP and define the value proposition.
As their products (or features) get closer to being launched, they create Go To Market plans to understand where and how they are reaching their customers.
Sample PM job description
2. Technical PM
At a high level, Technical PMs can be compared to a CTO.
They focus on HOW the solution works, and the engineering and research required to deliver the solution.
Technical PMs work on the "HOW" to deliver a product, driven by technical specs and engineers. TPMs are constantly concerned about designing solutions that require:
- Reliability and live-site availability.
- Data Protection and Compliance.
- Localization and Globalization.
- Security and Privacy.
- User Experience.
- Performance.
- Accessibility.
In their day to day, they are responsible for working with Engineers and other teams to make sure that projects are delivered. They manage the Product backlog and prioritize it.
Technical PMs also work closely with Engineers to triage bugs and help with engineering estimations. Their key focus is on their product performance metrics.
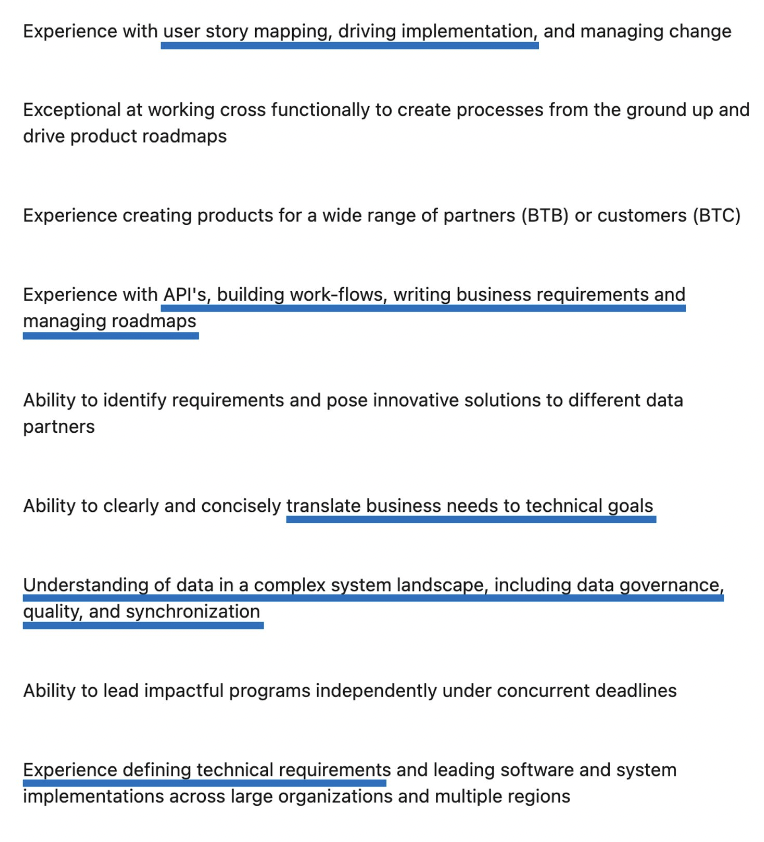
Sample Technical PM job description
3. Growth PM
Growth PMs are still finding their place within the industry. While their scope of work is more or less clear, few companies make a distinction in the title between PMs and Growth PMs.
The core responsibility of Growth PMs lies on expanding the product's client base, increasing revenue or pushing into new areas. They are responsible for specific metrics, more than they are responsible for specific features.
Growth PMs need to master experimentation (A/B testing) and cross-functional collaboration since they'll likely be constantly working with multiple teams.
Growth PMs are responsible for:
- A/B testing.
- Drive profit for the business.
- Encourage engagement in the product.
- Questioning and improving segmentation approaches.
- Customer Acquisition, Retention, and Upselling strategies.
- Tweaking onboarding experiences to reduce time to value.
Growth PMs oversee the entire customer journey, from Marketing and Acquisition to Loyalty and Expansion. They experiment and help prioritize high-impact initiatives.

Sample Growth PM job description
4. Data PMs
Data PMs focus on data, obviously, but not only on analyzing the data. They focus on the process to collect, organize, store and share data within the organization.
Their goal is to balance the strategy, governance, and implementation of anything related to internal data.
What does this mean?
Data PMs focus on the data flow throughout the entire product lifecycle. They use this data to help conversations between all the stakeholders involved (executives, engineers, analysts, other PMs) and even customers - everyone who will consume this data.
While products use data to be built, for Data PMs, their product is the data. In practice, this means that Data PMs can be part of any product team and this is what they do:
- A/B testing.
- Define OKRs and KPIs.
- Champion data literacy and insights.
- Track usage to identify opportunities.
- Do market research, user interviews, and testing.
While PMs do most of these for their Products, Data PMs do these for multiple teams, helping other PMs along the way.

Sample Data PM job description
See you next week!
Whenever you're ready, there are 3 ways I can help you:
- The best frameworks to ace your Product Manager interviews and get an offer here. (950+ students!)
- Schedule a 1:1 session with me for Mock Interviews and Career Guidance here.
- Promote your brand/business to 8K+ Newsletter subscribers by sponsoring content.
Helping Everyone To Land Their Next Product Manager Job
Join 8,000+ current and aspiring Product Managers in my Newsletter. Every email gives you a quick and actionable tip on landing your next Product Manager offer.
I hate SPAM. I will never sell your information, for any reason.


